Non-Ionising Radiation Information
What is Non-Ionising Radiation?
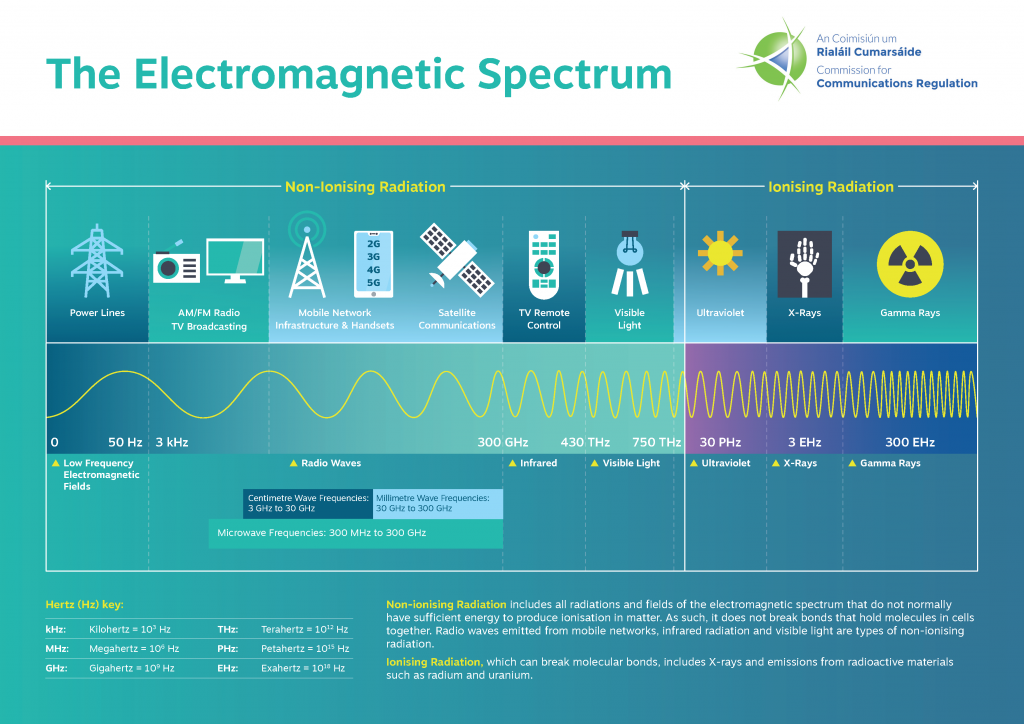
All radiation falls into two classifications – ionising and non-ionising.
Non-ionising radiation includes all radiations and fields of the electromagnetic spectrum that do not normally have sufficient energy to produce ionisation in matter. As such it does not break bonds that hold molecules in cells together. Types of non-ionising radiation for example include radio waves emitted from mobile networks, infrared radiation and visible light.
Ionising radiation includes X-rays and emissions from radioactive materials such as uranium and radium, see below:
Who recommends health protection standards for NIR?
The International Commission on Non-Ionising Radiation Protection (“ICNIRP”) recommends exposure limits for NIR in areas accessible by the general public. The main objective of this is to “establish guidelines for limiting EMF exposure that will provide protection against known adverse health effects”.
The current ICNIRP limits are set out in two documents available at the ICNIRP website [1] and [2]. The most recent ICNIRP guidelines [1] for limiting exposure to electomagnetic fields (100 KHz TO 300 GHz) was published on 11 March 2020. The same exposure limits apply whatever technologies emit the non-ionising radiation (for example 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, TV or FM/AM radio).
ICNIRP is funded by governments and public bodies and is totally independent of industry. Its work is endorsed by the World Health Organisation.
The European Commission has published Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on 5G on its website available at ec.europa.eu
What is ComReg’s role in relation to NIR?
ComReg manages Ireland’s radio spectrum which is a national resource used to provide a wide range of wireless communications services including radio and television broadcasting, mobile telephony, and wireless broadband. In managing the radio spectrum, ComReg obliges network operators under a Wireless Telegraphy Licence or a General Authorisation as applicable, to ensure that emissions from their networks do not exceed the public exposure limits established by ICNIRP.
As part of its spectrum management function, every year ComReg measures NIR levels in public areas at a minimum of 80 different sites, located throughout Ireland. These are chosen based on demographic and geographic factors. To date, over 1919 sites have been surveyed and NIR levels at all sites have been found, without exception, to fall well below the international limits for public exposure set by ICNIRP.
All of ComReg’s NIR measurement reports are available online at Siteviewer. ComReg’s most recent measurement reports can be found here.
Roles of other public bodies in relation to NIR
Department of the Environment, Climate and Communications (DECC)
DECC is responsible for setting policy relating to the health effects of Non-Ionising Radiation (NIR) including electromagnetic fields. For more information please see www.gov.ie/decc.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
The functions of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) include the provision of independent expert advice to the Government and to the public on exposure to NIR (including on relevant standards for public protection), as well as the monitoring of scientific/technological developments likely to impact on public exposure to NIR. For more information please see the EPA website at http://www.epa.ie/radiation/emf and the EPA’s brochure on “5G and Health
Local Authorities
The siting of telecommunications masts and equipment is a planning matter in respect of which ComReg has no statutory function or role. Planning at local level is the responsibility of local authorities. Please contact your local council if you seek information on the planning status of a mast or other telecommunications equipment in your area (e.g. if planning permission was required and, if so, who sought that permission). For more information please see http://www.housing.gov.ie/planning/.
Health and Safety Authority (HSA)
The HSA regulates exposure to NIR in the workplace in accordance with EU Directive 2013/35/EU. For more information please see https://www.hsa.ie/